Implant Dentistry
A dental implant (artificial tooth root) is a popular denture option after a tooth has been lost or extracted. Implants are surgically implanted in the jawbone, mirror the shape of a screw, and bond with natural bone. They form a basis for dental crowns (artificial teeth).
Dental implants are widely considered the most efficient permanent option for restoring the natural appearance and function of missing teeth.
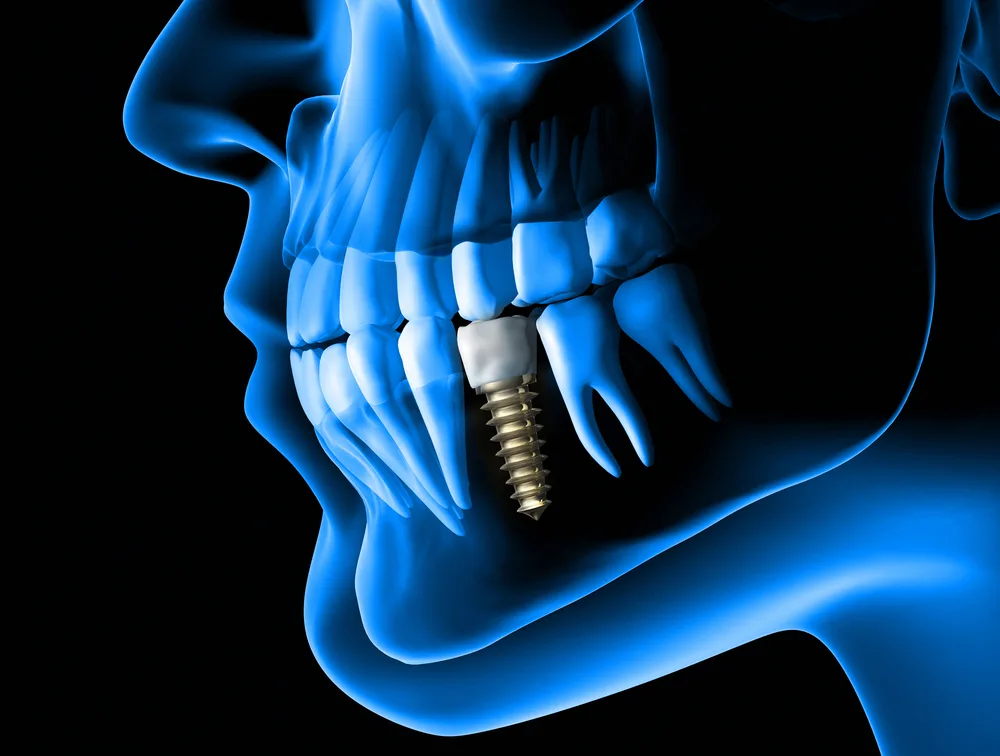
Types of Dental Implants
Endosteal (in the bone): These implants constitute screws, cylinders, or blades surgically placed into the jawbone. These kinds of implants are more often used for patients with bridges or removable dentures.
Subperiosteal (on the bone): These implants are placed along with metal frameworks on top of the jaw, these metal framework’s posts protrude through the gum to hold the prosthesis.
Digital Implant surgery
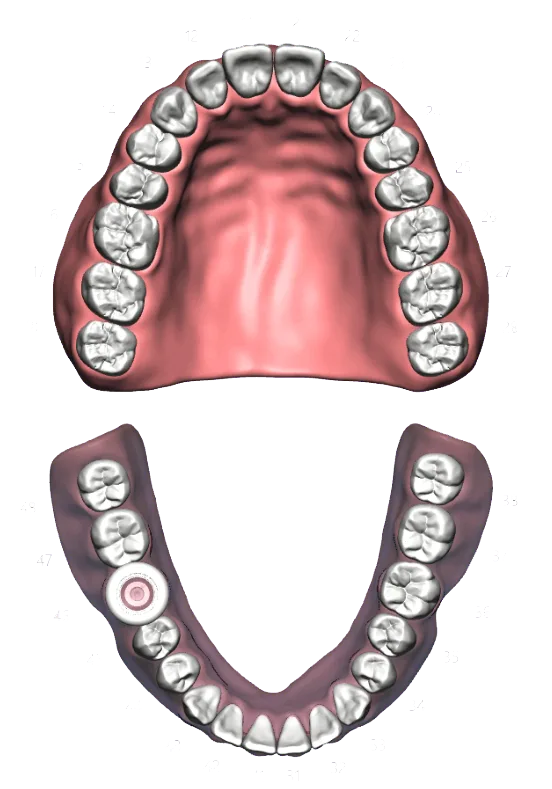
Digital implant surgery (also known as digital navigational implant surgery) uses 3D computer simulation to check the condition of the bones and the position of the nerves. With this information, a reputable cosmetic dentist can plan surgery with minimal incision. Since digital implant surgery focuses on the smallest possible incision, the pain is much less than with conventional implant surgery.
Difference between convention implant surgery and minimal incision surgery
Minimal incision surgery means the patients need minimal incisions to reduce their pain, discomfort, and recovery time. With dental implants, this means the cuts are so small that you don’t need stitches. Where as conventional implant surgery, the techniques require a surgical incision and recovery time can be slow and painful due to swelling and risk of infection.
Conventional Incision Surgery
Minimal Incision Surgery
With conventional dental implant surgery, the gum tissue must be cut over the entire length in which the implants are inserted. Because of this, many patients are now turning to digital implantation.